What is belly fluid retention?
Fluid retention in the belly occurs when there is excessive fluid accumulation in the abdominal region.
What are the symptoms of fluid retention in the belly?
Fluid retention in the belly, also known as abdominal edema, can present a variety of symptoms. These symptoms can vary in intensity and include:
- Bloating: Bloating is one of the most obvious symptoms of fluid retention in the belly. The abdominal area may appear distended, increased in volume and feel full;
- Feeling of Heaviness: Many people describe a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdominal region, as if they were carrying extra weight;
- Changes in Skin Texture: The skin in the affected abdominal area may feel tight, shiny, or even tender to the touch;
- Variations in Urine: In more severe cases of fluid retention, there may be variations in urinary patterns, such as urinating less frequently or having more concentrated urine;
- Changes in Laboratory Markers: In more severe or chronic cases of fluid retention, changes in electrolyte levels, such as sodium and potassium, can be observed in blood tests.
What are the causes of belly fluid retention?
Fluid retention in the belly can have several causes, including an unbalanced diet high in salt, lack of physical activity, hormonal imbalances, kidney problems, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, pregnancy and even certain medications.
Why does fluid retention affect women more?
Fluid retention in the belly can affect both men and women. However, many women report experiencing this problem more frequently and more intensely, especially at certain times in the menstrual cycle or during pregnancy. There are several reasons why women may be more prone to fluid retention in their stomach, including:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy can influence fluid balance in the body. Female hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, can affect sodium and water retention, contributing to bloating;
- Menstrual Cycle: Many women experience fluid retention during the premenstrual phase (premenstrual syndrome), when hormone levels fluctuate significantly;
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, rising hormone levels, along with the growth of the uterus, can put pressure on blood vessels and cause fluid retention in various parts of the body, including the belly;
- Lifestyle: Factors such as diet, level of physical activity and stress levels can play a role in fluid retention. Some eating habits and lifestyle choices can contribute to abdominal bloating;
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can also influence how the body regulates fluids and susceptibility to fluid retention;
- Age: As women age, hormonal changes associated with menopause can affect fluid regulation in the body;
- Use of Contraceptives: Some contraceptive methods, such as birth control pills, can cause fluid retention as a side effect.
How to prevent fluid retention in the belly?
Preventing fluid retention in the belly involves a combination of healthy habits and lifestyle adjustments. Although it is not always possible to completely avoid fluid retention due to hormonal factors and other variables, these practices can help reduce the frequency and intensity of abdominal bloating:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help the body eliminate excess fluids and toxins. Although it may seem counterintuitive, adequate hydration can actually help prevent fluid retention;
- Reduce Salt Consumption: Excessive salt consumption can lead to fluid retention. Avoid foods high in sodium, such as processed foods, fast food and snacks. Choose natural seasonings and herbs to enhance the flavor of food;
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, fiber and lean proteins can help balance fluid levels in the body. Potassium-rich foods, such as bananas and avocados, may also be beneficial;
- Avoid Inflammatory Foods: Foods that can cause inflammation, such as refined sugars, carbohydrates and processed foods, can contribute to abdominal bloating. Choose whole foods and anti-inflammatory nutrients;
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise can help improve circulation, stimulate lymphatic function and reduce fluid retention. Exercising regularly can help prevent abdominal bloating;
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can affect hormones and fluid regulation in the body. Practices such as meditation, yoga and relaxation can help reduce stress;
- Leg Elevation: Elevating your legs periodically throughout the day can help improve venous return and reduce swelling in the legs and belly;
- Adequate Rest: A good night’s sleep is important for hormonal regulation and fluid balance in the body;
- Avoid Excess Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption can contribute to dehydration and fluid retention. Consume these substances in moderation.
Treatments for fluid retention in the belly
Living Clinic offers effective treatments for fluid retention, including:
Lymphatic drainage massage
Lymphatic drainage is a therapeutic technique that stimulates the lymphatic system, helping to eliminate toxins and properly transport fluids from the body. This gentle, rhythmic massage promotes lymphatic circulation and helps reduce swelling, providing immediate relief.

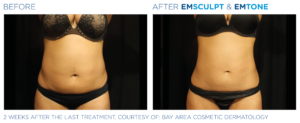
EMTone
EMTone is a revolutionary treatment that combines advanced radiofrequency and shock wave technologies to improve blood circulation, stimulate metabolism and reduce fluid retention. This non-invasive, painless approach delivers visible results, helping to tone the skin and reduce puffiness.
Schedule a free assessment to hear our professionals’ recommendations for your particular case and clarify all your doubts.
We are on Av. da Boavista, in Porto!



