Bariatric surgery is the most effective solution to combat obesity in our population, which has seen an epidemic growth. This fact has been well documented in the media. It is estimated that in Europe alone there are around 160,000,000 patients, where around 1,500,000 are children. It is also a fact that discrimination prevails over obese people whose self-esteem is at a very low level, leading to a lack of social engagement.
In a large proportion of these obese patients, both blood pressure and diabetes are altered, as well as other diseases that accompany them. This means that family doctors and surgeons are increasingly subjected to greater pressure in an attempt to combat this problem, either surgically or non-surgically, by patients seeking long-term and effective weight loss. Surgical intervention is arguably the most effective and long-lasting form of treatment for morbid obesity.
Bariatric surgery represents a unique discipline for several reasons, the first of which is that bariatric surgery is founded on the attempt to alter behaviours as well as physiology, unlike other reconstructive or resection surgeries. Furthermore, its success depends on the patient’s discipline and their adherence to the behavioural changes that the surgery imposes. Patients with morbid obesity often have multiple diagnosed problems because this is a pathology that affects almost all systems in the body.
Surgeons who treat morbid obesity quickly concluded that it is impossible to carry out this treatment without using a comprehensive and multidisciplinary program, developed by a diverse and dedicated group of people in the healthcare field, who can evaluate patients, as well as prepare them either mentally and physically for the surgery and the lifestyle changes that will be required of them.
To this end, there is a need to organize comprehensive programs that require a multidisciplinary approach and a large institutional commitment, leading to the formation of obesity treatment units or bariatric units, capable of playing an educational role and developing support strategies for patients.
Patients with BMI >/= 40, or 35 with comorbidities are generally eligible for surgery. Several weight loss attempts must have been made in the past, supervised by dietary regimens, exercise or medication. However, we have to consider that some patients with a BMI < 35 could be candidates, but they should be discussed within the entire team.
Although the age range between 18 and 60 years old does not pose any objection to surgical treatment, studies reveal that patients under 18 and over 60 years old, after being properly analysed, may be candidates for surgery. Therefore, age alone is not an objection to its achievement.
After surgery, close follow-up and a multidisciplinary approach are necessary for the success of a program of this magnitude. The knowledge of the program’s family doctors, their understanding of what bariatric surgery means, how it is performed and what is expected of it is fundamental for these programs to be successful, as they will always be the first to see this patient and tell them what they need.
Living Clinic’s bariatric surgery team is led by surgeon Dr. Luís Sá Vinhas.
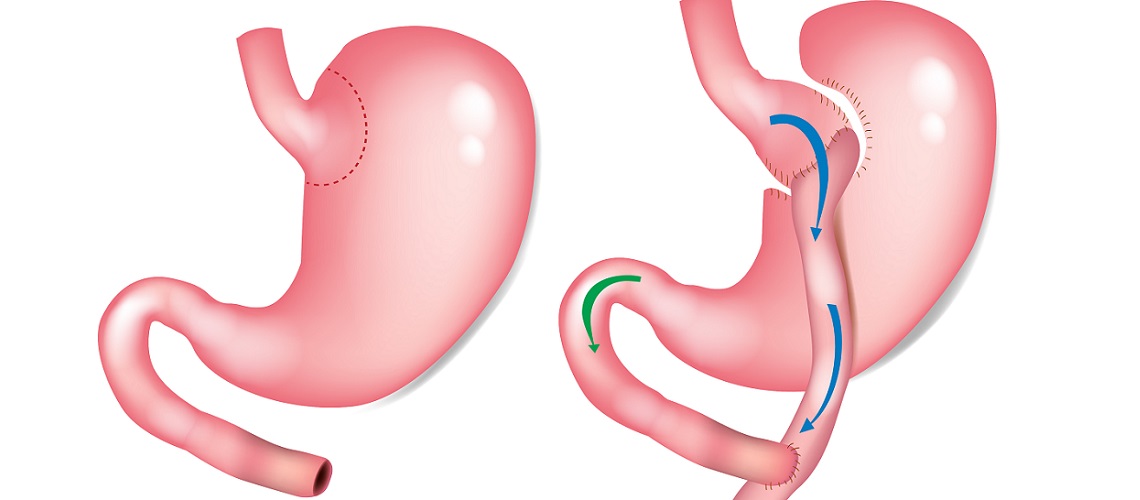
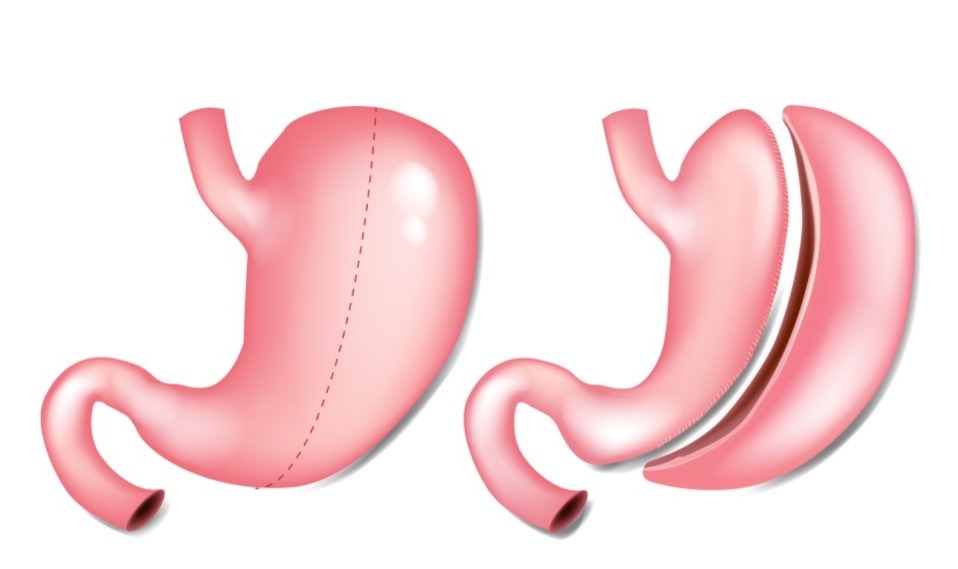
The most effective and popular techniques used in bariatric surgery today are Gastric Bypass and Gastric Sleeve.
Make an appointment to clarify all your doubts.